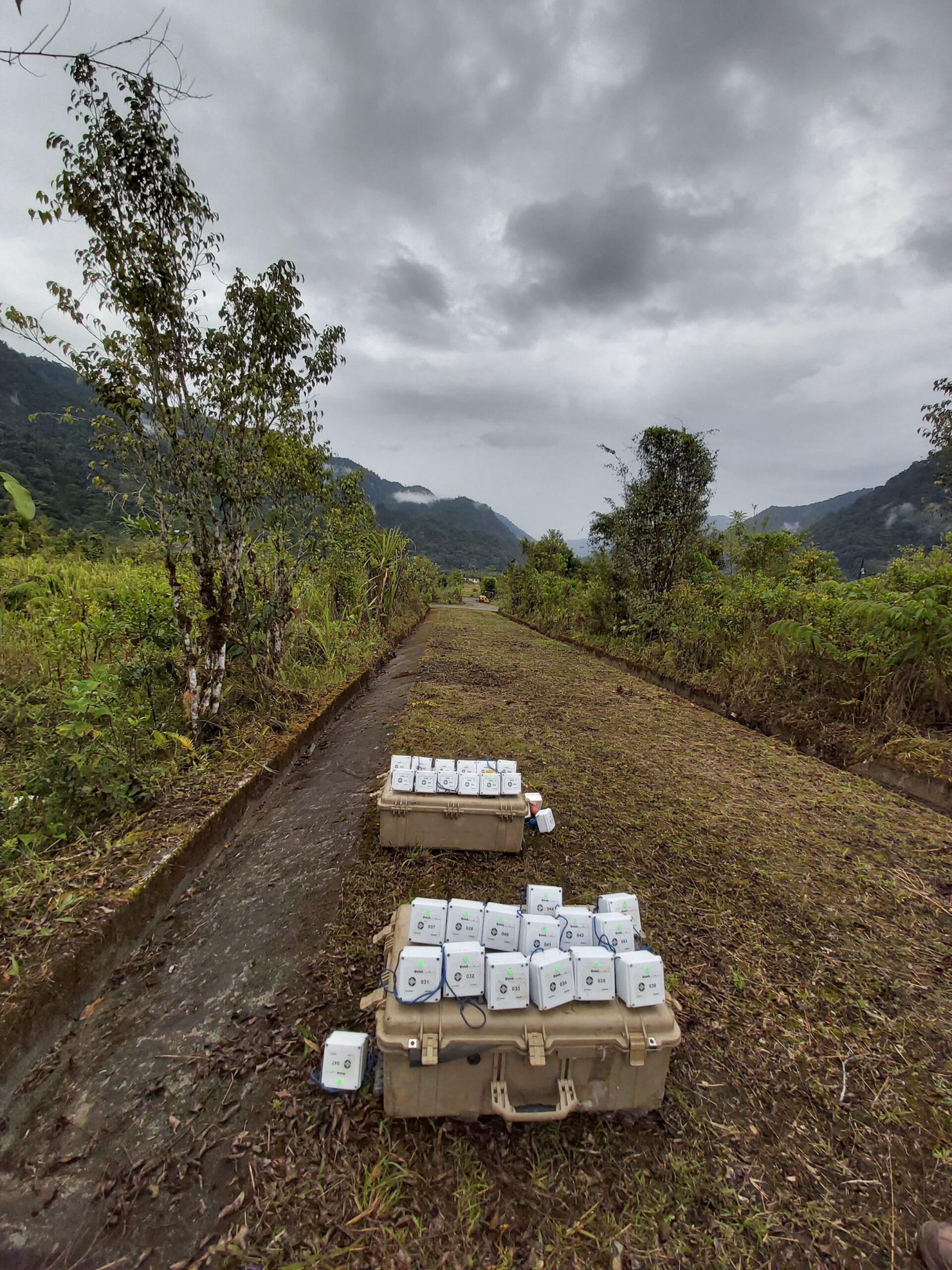
Shear Zone Exploration With Ambient Seismic Noise
GOAL
In Shear Zone Exploration With Ambient Seismic Noise, the objective is to discover and map shear zones through the use of passive seismic exploration techniques based on surface waves.
ZHEAR ZONES
A “shear zone” is a zone of closely spaced, approximately parallel faults that often channel solutions in the subsurface and may host large mineral deposits.
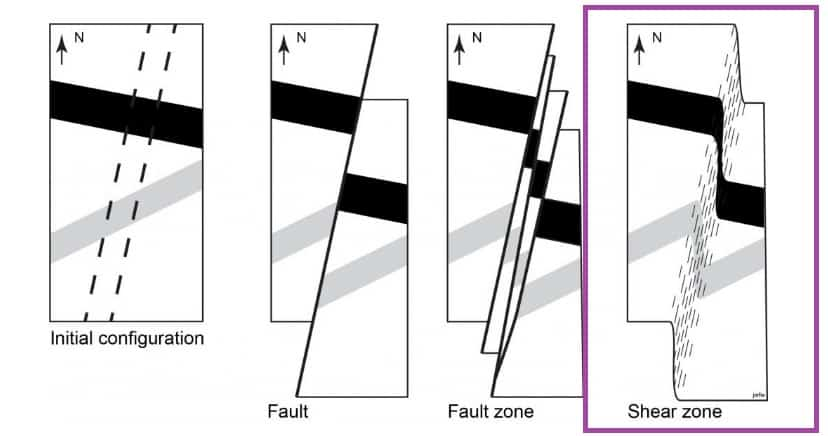
SCOPE
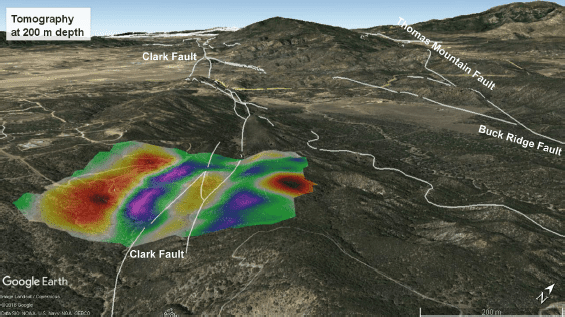
- Obtaining the shear wave velocity structure (Vs) in 1D, 2D and 3D, or monitoring over time (4D) by means of tomographic imaging techniques based on recording and analysis of surface waves by interferometry.
- Shear zones appear as sectors of low shear wave velocity (Vs). The edges of the shear zone are evident in the drastic change in seismic velocity.
- Depth of investigation and resolution determined, among other factors, by the nature of the noise, design and coverage of the sensor array, and seismic noise bandwidth.
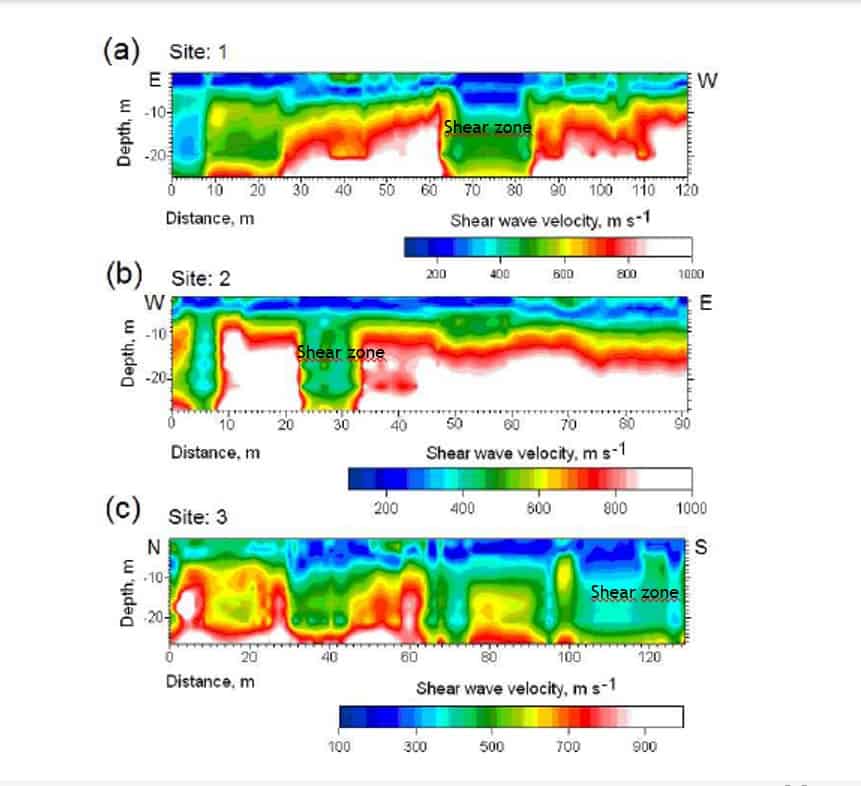
ADVANTAGES OF EXPLORATION WITH AMBIENT SEISMIC NOISE
- As it is a passive seismic technique, the factors inherent to active sources, such as perforation, power, permits and transportation, among others, are non-existent.
- Because the presence of environmental seismic noise can have a very large distribution and coverage, passive seismic is feasible at local, semi-regional, and even regional scales in both urban and remote settings. So, even far from urban environments and anthropic noise, the technique is feasible taking advantage of natural surface noise sources, such as waves, river flows, wind, and even earthquakes generated in tectonically active areas in the vicinity of the study area.
- Low acquisition costs compared to active seismic methods, even those from a non-explosive source.
- From surface waves, we have the ability to map lateral or vertical variations that correspond to low-velocity intervals, associated with faults, fractures, or shear zones.
- Minimal or non-existent environmental footprint.
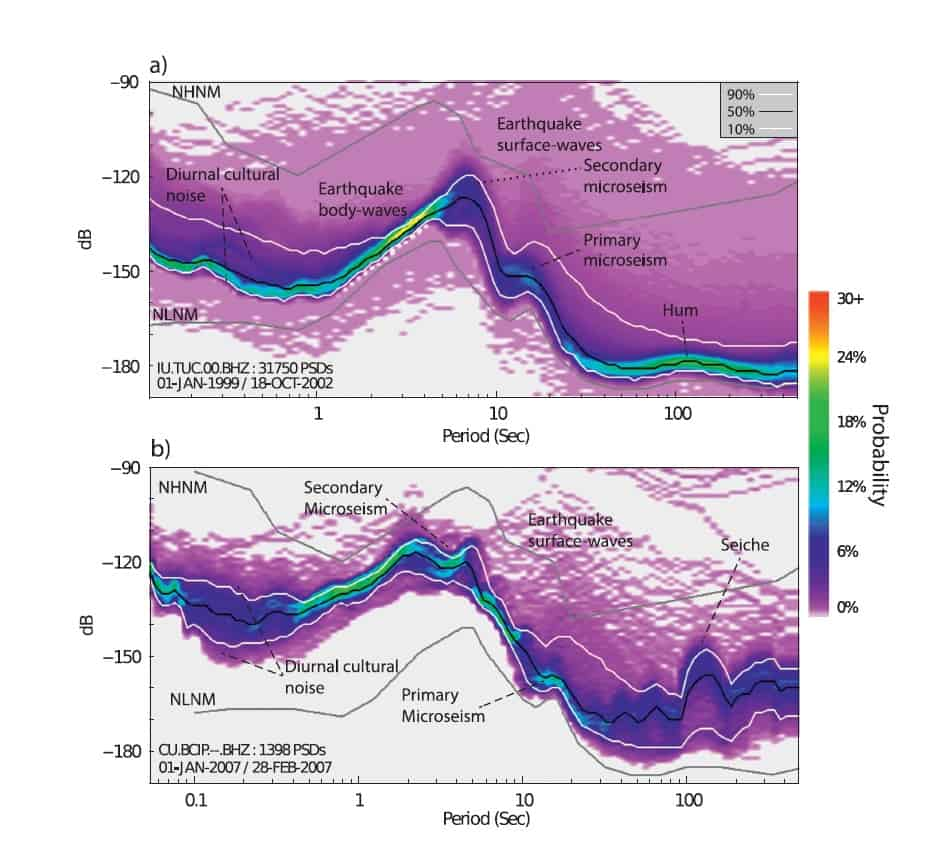
LIMITATIONS OF SHEAR ZONE EXPLORATION WITH AMBIENT SEISMIC NOISE
- Range in depth determined by the quality (amplitude and frequency) of the seismic noise present in the area.
- The feasibility, for semi-regional or regional studies, depends on nodal acquisition systems with prolonged autonomy. Wired seismograph systems have little feasibility of being used in large-scale (semi-regional or regional) surveys.
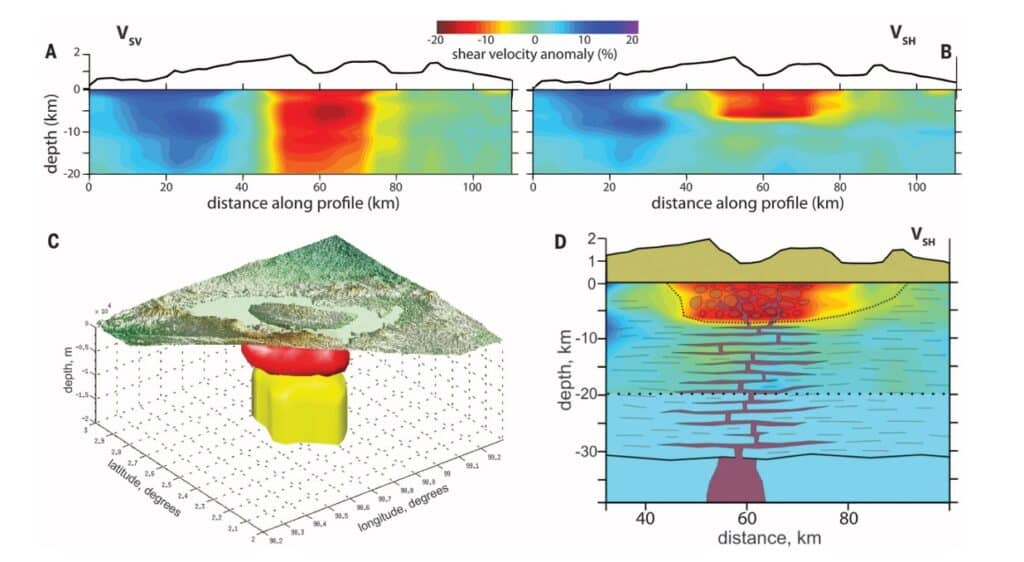
THE SUBSUELO3D ADVANTAGE
Our company is ideally suited to be your ally in Shear Zone Exploration projects Based on Ambient Seismic Noise for various reasons:
- We have hundreds of autonomous Quick nodes with very low instrumental noise, which is essential to reliably record seismic noise.
- We are experts in quality control of environmental seismic noise, thanks to internal developments such as the SPAC RT software.
- We accompany our clients in the acquisition design phase, modeling the seismic noise scenario, possible frequencies, and depth of investigation to be achieved with the Ambient Seismic Noise Tomography technique.
| Lithology | Vp (km/s) | Poisson’s Ratio | Vp/Vs | Vs (km/s) | F min (Hz) | DOI (km) |
| Pegmatite | 4.15 | 0.25 | 1.73 | 2.40 | 1.0 | 0.8 |
| Garnet Biotite Sillimanite Gneiss | 4.20 | 0.25 | 1.73 | 2.42 | 1.0 | 0.8 |
| Garnet Biotite Gneiss | 4.50 | 0.25 | 1.73 | 2.59 | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| Graphitic Mica Schist | 4.70 | 0.25 | 1.73 | 2.71 | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| Galena | 4.95 | 0.25 | 1.73 | 2.85 | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| Amphibolite | 5.30 | 0.25 | 1.73 | 3.06 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Mylonite zone | 5.25 | 0.25 | 1.73 | 3.03 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
Example of expected depth of investigation (DOI) modeling results, executed by Subsuelo3D for a major mining client.

